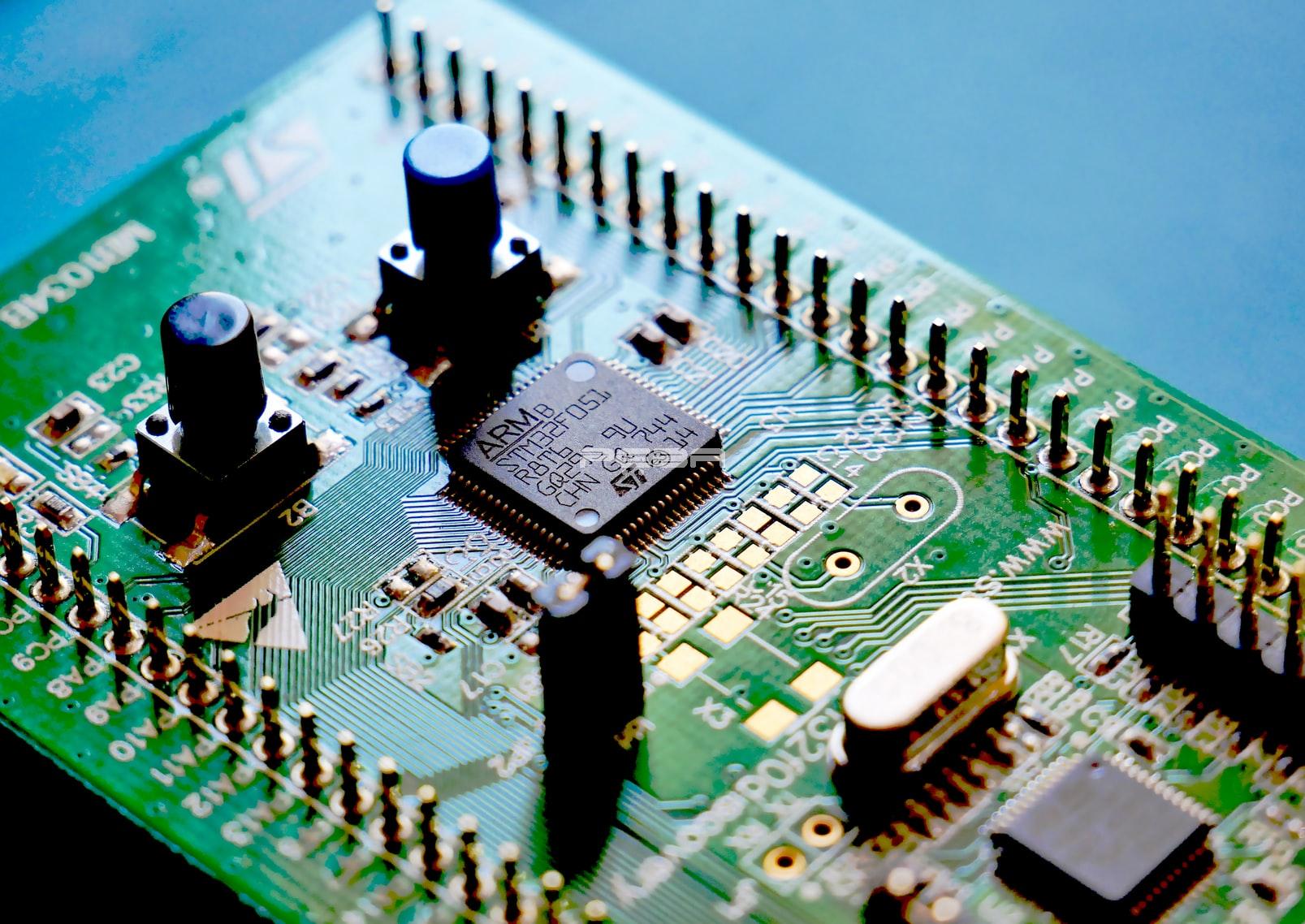
Machines, automobiles, computing terminals, PLCs, and other electronic devices rely on printed circuit boards (PCBs), which have steadily grown in size and efficiency over the last several decades to become a tiny, efficient, and critical component of the gadgets. Additionally, they have had a transformative effect on introducing discoveries, technologies, and ideas into the global electronics sector, resulting in a massive rise in productivity. The complexity of making high-quality printed circuit boards (china PCB) is demonstrated by their tiny footprint and superior reliability when electrically connecting individual electronic components in an electronics design. Surface mount technology (SMT) is the most extensively used PCB assembly technique in the modern world, representing a considerable development over previous assembly techniques such as through-hole assembly. In many ways, SMT assembly is now commonly recognized as the gold standard of PCB assembly processes.
For a multitude of reasons, SMT has overtaken prior manufacturing processes to become the dominant way of generating printed circuit boards, including the following:
Time efficiency
Before the widespread use of SMT assembly, point-to-point and through-hole assembly were used; however, these techniques required a significant amount of time because assemblers had to solder pads to the PCB’s frame and also solder connecting wires, which not only added time to the soldering process but also altered the way energy was transmitted throughout the china PCB. On the other hand, SMT assembly consumed less time since assemblers just needed to solder pads to the components. SMT avoids these challenges by connecting components to the surface of the PCB rather than through-hole connection sites, as traditional techniques do. This fundamental discovery permits the automated fabrication of printed circuit boards (PCBs) that is exceedingly time efficient.
Reduces assembly costs
Compared to automated SMT assembly, traditional PCB assembly procedures take a substantial amount of time. As a result, manufacturing PCBs used to be more expensive than it is now, owing to SMT assembly. Additionally, for low-volume or prototype PCBs, which design engineers typically demand, the cost of manufacturing even a small number of PCBs using traditional assembly procedures was prohibitively high. Due to automation and the ability to plan the manufacture of a variety of low-volume PCBs concurrently, SMT assembly can reduce manufacturing costs, enabling it to compete with lower-cost alternatives. Customers concerned about costs should always verify that the PCB assembly service they are seeking offers automated SMT assembly.
The usability has been enhanced
SMT PCBs include fewer components than earlier generations, allowing the overall PCB to be more compact and streamlined while also attaining better levels of energy efficiency. With these advantages, contemporary printed circuit boards (PCBs) may be used in a broader variety of devices, including portable and laptop computers, smartphones, and machines requiring a flat, compact PCB control board rather than a massive, multi-dimensional PCB control board. This is one of the reasons why SMT-manufactured printed circuit boards have gained universal acceptance across the industry, from electrical circuit designers to OEM machinery designers.
ChinaPCBOne Technology LTD. is the author of this article on PCB assembly. Find more information, about PCB manufacturing.